Table of Contents
Model Critique
Definition
Is: What it is
IsNot: What it is not
Rationale
- Models are not correct by virtue of inspection or by virtue that everybody worked on it.
- Many different ways to implement same function and inevitably there is a trade-off when a choice is made. A critique of a model provides an outsider's perspective
- Verify and validate the model for a given project, potentially as part of a non-advocate review
- Evaluate the current state and achievements on an MBSE effort to determine whether it requires or would benefit from additional funding
- Evaluate whether a sister project should adopt the MBSE approach based on the current MBSE efforts
- Evaluate a tool vendor
Performance Qualities
: How to determine the performance of {Thing}
Problem
: What issues are relevant to {Thing}
Precondition
: What conditions are necessary for {Thing} to operate
Postcondition
: What conditions are necessary for {Thing} to produce
Ontology
: What terms/taxonomy are relevant to {Thing}
Methodology
Method
Heuristics
- Is there a potential for failure due to timing?
- Has the model used patterns?
- Does different components react differently to different stimuli
- Is there consistency
- Look at interfaces between SOI and context
- What are the system dynamics and failure
- What are the rainy day scenarios
- Do observations on numbers
Proofs
Process
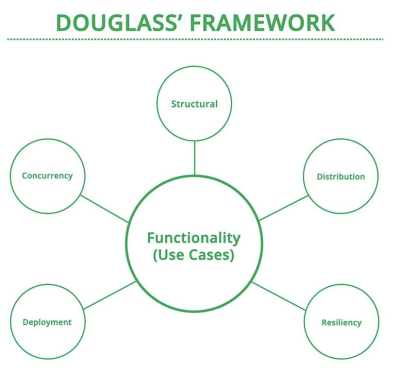
- Functionality and Use Cases
- What are the preconditions for the function
- Is there any validation vs requirements
- What happens in case of error/illegal use csae
- Structure of the Model
- Interfaces
- Dependability and Failure Modes
- Check for any broken/circular relationship/redundant content
- Touches on security/availability
- What failure modes are anticipates
- Has the modeler tested for resilience to failure mode
- Concurrency Analysis
- There are two types concurrency failure (livelock and deadlock)
- Livelock - When an element constantly changing resulting in a “runaway” state preventing model convergence
- Deadlock - Two components attempt to share a common resource, blocking access to both
- It is possible to be under-specified and over-specified
- Management and Deployment
- Has allocated logical to function to structure
- Who has authority to make changes?
- Has model lifecycle management process been documented?
- Review Against Qualities of Great Models
Parts
Outputs
- Remarks on whether the model is meeting the intended scope and purpose.
- Set of observations and data on the model’s strengths and weaknesses. Your findings should relate back to specific instances of the model with data sampling to backup your feedback.
- An evaluation against each of the qualities of great models, as well as supplementary behaviors or qualities you believe are relevant for an MBSE model.
- Conclusions and recommendations for the specific rationale for the critique.